Rheometer
M5600 HPHT Rheometer
.jpg) M5600 HPHT Rheometer (Carbon Block Bath Option)
M5600 HPHT Rheometer (Carbon Block Bath Option)
 M5600 HPHT Rheometer (Oil Bath Option)
M5600 HPHT Rheometer (Oil Bath Option)
.jpg) Proppant Slurry Testing Accessory Kit
Proppant Slurry Testing Accessory Kit
 (Medium).jpg) Proppant Slurry Testing Accessory Kit (Top View)
Proppant Slurry Testing Accessory Kit (Top View)
.jpg) Clear Sample Cup
Clear Sample Cup
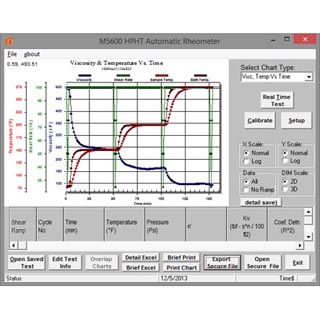 M5600 Rheometer PC Software
M5600 Rheometer PC Software
 Software of Dynamic Testing 1
Software of Dynamic Testing 1
 Software of Dynamic Testing 2
Software of Dynamic Testing 2
 Software of Dynamic Testing 3
Software of Dynamic Testing 3
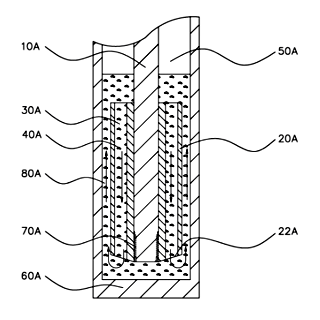 Special U.S. Patented Hollow Bob
Special U.S. Patented Hollow Bob
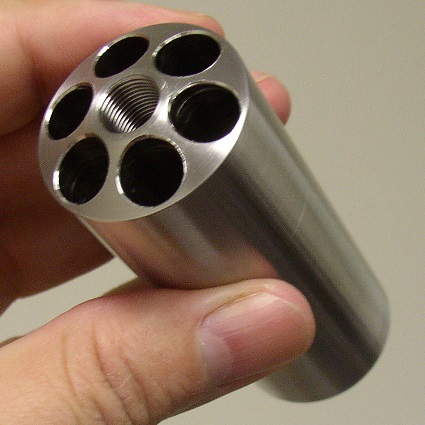 M5600 Hastelloy HB5 Hollow/Oscillatory Bob (included with the oscillatory option)
M5600 Hastelloy HB5 Hollow/Oscillatory Bob (included with the oscillatory option)
.jpg)

.jpg)
 (Thumbnail).jpg)
.jpg)





- Height: 25.5 in.
- Width: 12.5 in.
- Depth: 8.5 in.
- Weight: 66 lbs with oil bath (61 lbs with carbon block)
- Max Pressure: 2,000 psi | Max Temp: 500°F (260°C)
- U.S. Patent No.: 6,938,464
U.S. Patent No.: 6,951,127
U.S. Patent No.: 9,157,846
Rotational viscometer with direct-coupled torque transducer - no bearings
The Grace Instrument M5600 HPHT Rheometer is a true Couette, coaxial cylinder, and rotational rheometer, operating at high pressures up to 2,000 psi and temperatures up to 500°F (260°C).
The unit incorporates a direct drive between the bob shaft and the torque transducer, which eliminates moment of inertia errors usually associated with magnetically coupled torque transducers.
Thus, the torque transducer can respond quickly and consistently to
changing bob shaft torque, resulting in lower maintenance costs while allowing continuous testing of corrosive samples.
The only true rheology measurement under pressure
Other rheometers often utilize a magnetic coupling across a pressure vessel to rotate a magnet on a bob shaft, using metal or air bearings, in order to measure viscoelasticity; however, when the tested fluid possesses different G'/G" values compared to the calibration fluid, the G'/G" measurement will be invalid.
A calibration fluid with known G'/G" values must be tested properly to provide a baseline for viscoelastic measurement.
The M5600 HPHT Rheometer does not employ magnetic coupling, instead taking direct measurements inside the pressure vessel, providing true measurement in a pressurized environment.
Viscoelastic option available for G', G" and phase angle testing
The M5600 HPHT Rheometer is also available with an optional viscoelastic module that performs viscoelasticity tests to derive G', G”, G* and phase angle.
This vastly increases the researcher's ability to predict the behavior of fluids, such as their capacity for suspending and carrying solids (weight material sag, drill cuttings transport, proppant transfer, etc.) This allows us to offer the M5600 dynamic option, which enables the user to perform true G' and G" viscoelasticity tests under pressure, without having to pre-test using fluids with known G'/G" values.
Cutting-edge database software enables customized search and data comparison
The application software, M5600 PC, includes powerful database tools for searching, categorizing, and comparing test results. The search criteria can include any test result parameter, including additives, descriptions, or other details.
M5600 PC also allows you to overlap as many test charts as you like. Each test chart will display with customized graphics to differentiate it from other tests.
Patented hardware design & detailed engineering lead to highly consistent data
The unique hardware and software design of the M5600 enable it to produce test results that are extremely repeatable, because process errors and other complications are eliminated by the robust and innovative configuration of hardware and software.
By removing contamination and other interference from the test environment, the M5600 test results reflect the properties of the test fluid instead of the properties of the testing hardware.
Special U.S. patented hollow bob can test rheology and helps overcome the Weissenberg Effect
The M5600’s oscillatory option includes a special, U.S. patented hollow bob that allows researchers to test the rheology of non-Newtonian fluids and help overcome the Weissenberg effect.
The bob design features off-centered axial direction holes, which creates a circulation path to refill the gap in the measurement zone should the liquid sample in the cup climb out, due to the Weissenberg effect.
Because of the differential shearing at the bottom of the cup and the bob, along with the pressure difference if the measurement gap is vacant, tested fluid tends to refill the measurement zone and recirculate along the measurement zone if the Weissenberg effect occurs.
Thus, the configuration of the hollow bob enables repeatable and reliable test operation using a broad selection of test fluids, methods, and environments.
| U.S. Patents: 6,938,464 U.S. Patents: 6,951,127 U.S. Patents: 9,157,846 |
| Dimensions: 8.5" Depth x 12.5" Width x 25.5" Height |
| Weight: 66 lbs (with bath) or 61 lbs (with carbon block) |
| Pressure Range: Atm to 2,000 psi |
| Sample Size: 32 to 78 ml |
| Resolution: 0.01% of full scale range or better |
| Temperature Range: Ambient (20 °F with Chilling Device) to 500°F (260°C) |
| Speed Range: 0.0001 to 1,100 rpm continuous |
| Frequency Range: 0.01 to 5 Hz (Optimized at 0.2 to 3 Hz) |
| Amplitude Range: 0.1% to 500 % (Optimized at 0.2% to 500%) |
| Shear Rate Range: 0.00004 to 1870 sec-1 |
| Shear Stress Range: 1 to 15,000 dyn/cm2 |
| Viscosity Range: 0.5 to 5,000,000 Centipoise |
| Torque: 14 μN.m to 100 mN.m |
| Repeatability: ±0.05% of full scale range or better |
| Voltage: 110-120V AC (220-240V AC with Transformer)*
*A 220-240V AC supply requires a step-down transformer, which is included if required. If unsure if your power supply setup is appropriate, or if there are any questions or doubts, contact Grace Instrument for assistance before plugging anything in. |
| Construction: Hastelloy C Wetted Material |
| Wattage: 600 W |
| Frequency: 50-60 Hz |
| Operating System Requirements: Windows 9X/2000/XP/Vista/7/8/8.1/10 |
- Allows the user to test samples with high acid concentrations, including fluids with 30% HCl
- All wetted materials are Hastelloy C276 construction
- Incorporates years of research into its innovative design
- Oil or dry heat option
- Fully digital with LCD screen
- Fast test cycle: Setup-load-test-clean
- Safety feature of temperature controller will stop heating if it sees temperature is above 520°F.
- Separate thermostat from temperature control loop that will cut off bath heater power supply when its temperature is above 500°F (260°C)
- Includes 2 temperature controllers, one for control, the other for safety.
- Over pressure relief valve
- Repeatable results with Test flexibility
- Includes M5600 PC™ software, which connects the M5600 with a Windows®-based PC
- Tests are simple to set up and run
- Customizable charts and real-time data are displayed during tests
- Saved tests can be searched by any specified test parameter: test name, fluid ID, additive, researcher name, or more
- SBC software on unit will stop heating if it sees temperature is too high
- PC software will send stop heating command it if sees temperature is too high.
- Also available: M5600 HPHT Rheometer Carrying Case (which has wheels and an extendable handle for easy transportation)
- Each M5600 unit has multiple thermocouples, dedicated thermostat for over heating shutoff, special relief valves, integrated N2 regulator, all internal tubing rating for 10ksi, and pre-programmed shutoff points within M5600 software.
- The new carbon bath is much cleaner than older oil bath and allows for heating at 2x rate.
- The M5600 HPHT Rheometer is completely compliant to API 13 & 39 specified geometry.
- It incorporates a direct measurement torque transducer and a separately controlled strain mechanism, which eliminates moment of inertia errors. These errors are often associated with magnetic coupling across a pressure vessel wall in a typical rheometer under high temperature and high pressure conditions.
- The M5600 HPHT Rheometer enables tests to obtain values for G' and G", N' and K', all with the same API geometry.
- Hastelloy C construction on wetted parts and multiple patented technologies enable it to test the most corrosive samples, including acids.
- M5600 PC™ software allows both single- and multi-step real-time testing.
- Standard rotational testing measures fluid viscosity under a constant shear rate (constant speed), which indicates only apparent viscosity, or how thick a fluid is. On the other hand, almost all drilling muds, fracturing fluids and cements have some "gelly" strength that enables them to suspend solid particles. This ability to suspend solids is very important to many oil field operations. The M5600 HPHT Rheometer oscillatory testing option provides the capability to measure how "gelly" a sample is, in addition to how thick the sample is, by providing G', G", and other data. 'This vastly increases the researcher's ability to predict the behaviors of these fluids, such as capacity for carrying solids (weight material sag, drill cuttings transport, proppant transfer, etc.). Oscillatory testing mode also completely removes measurement errors due to sample climbing.
- The M5600 HPHT Rheometer features patented technology that can directly measure the true viscoelasticity of a sample under high temperature & high pressure conditions without magnetic coupling-induced measurement errors
- The M5600 HPHT Rheometer unit comes equipped with an API 39 standard size rotor and bob, designated "R1B5", or rotor 1, bob 5. The B5 bob is very commonly used for fracturing fluid testing. To reduce sample climbing ("Weissenberg effect"), extended bobs, such as the XB5 and XB2 are recommended for testing crosslinked fluids or high molecule structure samples. For drilling fluids testing, we recommend the B1 bob.
Downloads for the M5600 HPHT Rheometer:
Read more about our instrument's technical applications within these scientific and academic publications:
-
SPE-213840-MS 2023
New Visco-Elastic Surfactant Formulation with Excellent Carrying Properties in Multiple Brine Systems and Wide Temperature Ranges
Rheological properties of multiple brine systems were measured with a Grace M5600 Rheometer.
https://onepetro.org/SPEOCC/proceedings-abstract/23OCC/2-23OCC/D012S003R001/521044
-
SPE-214203-MS 2023
Evaluation and Optimization of A Novel High-Density and High-Temperature Resistance VES-Based Fracturing Fluid
Rheological properties of VES fluids were measured with a Grace M5600 Rheometer.
https://onepetro.org/SPEGOTS/proceedings-abstract/23GOTS/2-23GOTS/D021S020R003/517901
-
SPE-211422-MS 2022
Novel Organically Modified Nanoparticles Stabilized Emulsified Acid Paves Way for Productivity Enhancement in High Temperature Gas Reservoirs
Viscosity of live emulsified acid samples were measured with a Grace M5600 Rheometer.
https://onepetro.org/SPEADIP/proceedings-abstract/22ADIP/3-22ADIP/D031S085R003/513101
-
MRS Communications, September 2021, Volume 11, 783-789 2021
Dynamic Mechanical Thermal Analysis of Thermoset Hydrogels
Viscoelasticity of thermoset hydrogels were measured with a Grace M5600 HPTHT Rheometer.
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1557/s43579-021-00087-z
-
SPE-206297-MS 2021
A Novel Gemini Cationic Viscoelastic Surfactant-Based Fluid for High Temperature Well Stimulation Applications
Viscosity of deaerated gels were measured with a Grace M5600 Rheometer.
https://onepetro.org/SPEATCE/proceedings-abstract/21ATCE/3-21ATCE/D031S056R006/469594
-
OTC-30967-MS 2021
Nanomaterials Improve Polymer-Based Gravel-Packing Fluids at High Temperature
The rheological measurements of an oxidative breaker with gravel-packing fluid was performed with a Grace M5600 Rheometer.
https://onepetro.org/OTCONF/proceedings-abstract/21OTC/1-21OTC/D012S059R019/466593
-
SPE-196357-MS 2020
Fracturing Fluid and Geomechanics Integration Solves Hydraulic Fracturing in the HP/HT Triassic – Jurassic Petroleum System, Krishna Godavari Basin, India Petroleum System, Krishna Godavari Basin, India
A baseline test of fracturing fluid rheological properties were performed with a Grace M5600 Rheometer.
https://onepetro.org/SPEAPOG/proceedings-abstract/19APOG/2-19APOG/D021S009R003/217229
-
SPE-201433-MS 2020
New Developed Mathematical Model for Predicting Viscosity Profile and Proppant Transport Utilizing HVFRs Dosage with Produced Water
Fracturing fluid rheology was measured with a Grace M5600 HPHT rheometer.
https://onepetro.org/SPEATCE/proceedings-abstract/20ATCE/2-20ATCE/D022S061R011/449882
-
OTC-30712-MS 2020
New Generation Fracturing Fluid
Rheological measurements of fracturing fluid in tap water was calculated with a Grace M5600 HPHT Rheometer.
https://onepetro.org/OTCONF/proceedings-abstract/20OTC/3-20OTC/D031S040R004/107404
-
SPE-199231-MS 2020
A Novel Nanotube/VES-Based High Temperature High Pressure Fracturing Fluid
Rheological measurements of NMR solvent were carried out with a Grace M5600 Rheometer.
https://onepetro.org/SPEFD/proceedings-abstract/20FD/1-20FD/D011S001R002/447076
-
IPTC-19601-MS 2020
NMR Investigation of Viscoelastic Surfactants Compatibility with Corrosion Inhibitors
Viscosity measurements of viscoelastic surfactants were carried out with a M5600 Rheometer from Grace Instrument Company.
https://onepetro.org/IPTCONF/proceedings-abstract/20IPTC/2-20IPTC/D021S026R003/154428
-
SPE-197748-MS 2019
Correlated Friction Reduction and Viscoelastic Characterization of Utilizing the Permian Produced Water with HVFRs during Hydraulic Fracturing
HVFR viscosity profiles were measured with a Grace M5600 Rheometer.
https://onepetro.org/SPEADIP/proceedings-abstract/19ADIP/4-19ADIP/D041S120R002/216525
-
SPE-197081-MS 2019
A Comprehensive Review of Formation Damage Caused by High-Viscosity Friction Reducers: Wolfcamp Case Study
A Grace M5600 Rheometer was used to test viscoelastic behavior of tested fluid by testing dynamic oscillatory frequency.
https://onepetro.org/SPELRBC/proceedings-abstract/19LRBC/2-19LRBC/D022S010R003/217983
-
SPE-196014-MS 2019
Viscoelastic Characterization Effect of High-Viscosity Friction Reducers and Proppant Transport Performance in High-TDS Environment
A Grace M5600 Rheometer was used to test dynamic oscillatory frequency of tested fracturing fluids.
https://onepetro.org/SPEATCE/proceedings-abstract/19ATCE/1-19ATCE/D011S013R002/217613
-
Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, Volume 173, February 2019, 1332-1339 2019
Crosslinked polymers as “smart” viscosifiers used in hostile environments
In this study the rheological properties of solutions containing “smart” viscosifiers under high temperature and high pressure were investigated. The Grace Instrument M5600 HPHT Rheometer, a coaxial cylinder, rotational, high pressure high temperature (HTHP) rheometer, was used. The pressure was kept constant in each experiment while the temperature was ramped up from room temperature to 180°C and kept for at least 3 hours. This allowed the analysis of the effect of temperature on the performance of the “smart” viscosifiers under HPHT conditions.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S092041051830980X
-
Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, November 2018, 57, 50, 17043-17047 2018
Constitutionally Dynamic Oil Well Construction Fluids-Metalloaminal Chemistry
Shear modulus rheological measurements were performed on a Grace M5600 HPHT rheometer with a circulating oil bath heater and pressurized with nitrogen to 3.4 MPa.
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/pdf/10.1021/acs.iecr.8b04019
-
SPE-191689-MS 2018
Factory Model Approach for Successful Coil Tubing Unit Drillout Operations in Unconventional Horizontal Wells
A Grace M5600 Rheometer was used to calculate the fluid rheology and viscosity of a fluid system used for drilling.
https://onepetro.org/SPEATCE/proceedings-abstract/18ATCE/2-18ATCE/D021S018R003/213755
-
SPE-191749-MS 2018
High-TDS Produced Water-Based, Low-Damaging Fracturing Fluids for Applications at 300°F or Higher
A Grace M6500 Rheometer was used to measure the viscosity of fracturing fluids.
https://onepetro.org/SPEATCE/proceedings-abstract/18ATCE/2-18ATCE/D021S020R006/213830
-
Carbohydrate Polymers, Volume 195, September 2018, 53-62 2018
Biopolymer from marine Athelia and its application on heavy oil recovery in heterogeneous reservoir
The viscosity against sheer rate was measured with M5600 HPHT rheometer (Grace Instrument, USA) at the wide range of temperature and salinity.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0144861718304478
-
Fuel, Volume 220, May 2018, 481-489 2018
Green phenolic amphiphile as a viscosity modifier and asphaltenes dispersant for heavy and extra-heavy oil
The effects of asphaltense and ACC on viscosity behavior of the heavy oil sample were studied at various temperatures and shear rates using a Grace instrument M5600 high pressure/high temperature rheometer equipped with an oil bath for temperature control.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0016236118301224
-
SPE-192191-MS 2018
Optimizing the Gel Strength of Water-Based Drilling Fluid Using Clays for Drilling Horizontal and Multi-Lateral Wells
The rheological properties such as apparent viscosity, plastic viscosity, and yield point were measured using M5600 HPHT rheometer (Grace Instrument).
https://onepetro.org/conference-paper/SPE-192191-MS
-
SPE-190029-MS 2018
Safe Boundaries of High-Temperature Fracturing Fluids
A Grace M5600 Rheometer was used to measure the viscosity of fracturing fluids.
https://onepetro.org/SPEWRM/proceedings-abstract/18WRM/4-18WRM/D041S007R006/215326
-
SPE-189540-MS 2018
Improving Wormholing Efficiency in Carbonates with a Novel System Based on Hydrochloric Acid
A Grace M5600 Rheometer was used to measure the viscosity of emulsified acid.
https://onepetro.org/SPEFD/proceedings-abstract/18FD/1-18FD/D012S007R001/214849
-
SPE-189563-MS 2018
High-Temperature Viscoelastic Surfactant Fluids with Low Scaling Tendency and Based on Seawater, Produced Water, or Brines
A Grace M5600 Rheometer was used to measure the viscosity and rheological properties of VES fluids.
https://onepetro.org/SPEFD/proceedings-abstract/18FD/1-18FD/D011S005R006/214905
-
SPE-189554-MS 2018
A Novel Viscoelastic Surfactant Fluid System Incorporating Nanochemistry for High-Temperature Gravel Packing Applications
A Grace M5600 Rheometer was used to measure the viscosity of HT-VES fluids.
https://onepetro.org/SPEFD/proceedings-abstract/18FD/2-18FD/D021S012R001/214925
-
SPE-184551-MS 2017
Nanomaterials-Enhanced High-Temperature Viscoelastic Surfactant VES Well Treatment Fluids
The oscillatory rheology of the VES fluids was carried out with the Grace M5600 to measure their stress response to the imposed sinusoidal shear deformations. The viscoelastic behavior of the fluids was characterized by the storage modu us (G’) and oss modu us (G”) corresponding to the so id-like and fluid-like contributions to the stress response of the fluids, respectively.
https://www.onepetro.org/conference-paper/SPE-184551-MS
-
SPE-183768-MS 2017
The Evaluation of Micronized Barite As a Weighting Material for Completing HPHT Wells
Rheology measurements were also conducted at HPHT conditions using GRACE M5600 rheometer to investigate the effect of barite particle size on fluid rheology at that condition.
https://www.onepetro.org/conference-paper/SPE-183768-MS
-
SPE-183652-MS 2017
Rheological Study of a Novel Sulfobetaine Surfactant-Based Acid System
A rotational, high pressure-high temperature (HPHT) rheometer (Grace Instrument, Model 5600) was used to measure the apparent viscosity of the live and spent acids. The viscometer allows working under conditions up to 1000 psi and 500 °F.
https://onepetro.org/conference-paper/SPE-183652-MS
-
SPE-181786-MS 2016
Development of Seawater-Based Fracturing Fluid for High-Temperature Wells
The cup was placed over a R1/B1 rotor/bob on a Grace Instrument rheometer set up to run at a 511 s-1 shear rate for 60 minutes at room temperature.
https://onepetro.org/conference-paper/SPE-181786-MS
-
SPE-180435-MS 2016
New Viscoelastic Surfactant with Improved Diversion Characteristics for Carbonate Matrix Acidizing Treatments
Viscoelastic surfactants (VES) have been used to replace polymer-based fluids in frac-packing, acid fracturing, and matrix acidizing. Rheology measurements were conducted on the VES-acid system. A Grace 5600 rheometer was used to conduct all viscosity measurements as a function of temperature.
https://www.onepetro.org/conference-paper/SPE-180435-MS
-
SPE-180402-MS 2016
Maximizing Performance of Residue-Free Fracturing Fluids Using Nanomaterials at High Temperatures
To measure the viscosity of each of the fracturing fluid systems under reaction conditions designed to simulate those in a high temperature and high pressure subterranean reservoir formation, sample volumes of about 100 mL were generally prepared for each test and 52 mL aliquots of each fracturing fluid system were injected into a Grace M5600 HPHT rheometer equipped with a B5 bob configuration.
https://www.onepetro.org/conference-paper/SPE-180402-MS
-
SPE-180215-MS 2016
The Effect of Chelating Agents on the Use of Produced Water in Crosslinked-Gel-Based Hydraulic Fracturing
Investigation of the effect of different chelating agents on the use of high-TDS produced water in high pH borate-crosslinked gels used in hydraulic fluid. Apparent viscosity of hydraulic fracturing fluid was measured at 180°F and at 300psia. Test performed at constant shear rate of 100s-1 with shear ramps (75, 50, 25, 50 and 75 s-1) repeated every 30 minutes.
http://dx.doi.org/10.2118/180215-MS
-
SPE-179553-MS 2016
Laboratory Study on Using Produced Water in High pH Borate Gels Used in Hydraulic Fracturing
Investigation of the fesibility of using produced water to formulate crosslinked-gel-based fracturing fluid. All apparent viscosity measurements of the of produced-water-base fracturing fluid were conducted at a temperature of 180°F and a pressure of 300psia. All test were conducted with B5 bob and 52 cc fluid volume.
http://dx.doi.org/10.2118/179553-MS
-
SPE-177469-MS 2015
Reduced Polymer Loading, High Temperature Fracturing Fluids using Nano-crosslinkers
The viscosity of gel samples with different nano-crosslinker concentrations were tested at high HPHT conditions to investigate the influence of the nano-crosslinkers on a gel's ability to suspend proppant.
http://dx.doi.org/10.2118/177469-MS
-
SPE-174363-MS 2015
New Al-based and Dual Cross-linkers to Form a Strong Gel for Hydraulic Fracturing Treatments
Investigation of the effects of various parameters including polymer loading, aluminum-based and aluminum-zirconium crosslinker concentrations, pH, and temperatures on rheological properties to achieve an ideal hydraulic fracturing fluid.
http://dx.doi.org/10.2118/174363-MS
-
SPE-174204-MS 2015
A New Fracturing Fluid for HP/HT Applications
Investigation of the effects of viscosifier concentration, temperature and salts on rheological properties and proppant suspending ability of V1-based fluid. The apparent viscosity of the fluids were measured at different temperatures (75, 245, 295 and 350°F). Both rotor and bob of the rheometer were made of Hastelloy C to resist acid corrosion.
http://dx.doi.org/10.2118/174204-MS
-
SPE 173745 2015
Viscoelastic Behavior and Proppant Transport Properties of a New High Temperature Viscoelastic Surfactant-Based Fracturing Fluid
New surfactant technology combining Gemini cationic and anionic surfactants in water, allows for a more effective viscoelastic surfactant system which is able to gel and maintain desirable viscosity at temperatures up to 275°F. M5600 was used to measure rheology of the surfactant gel at a temperature range of 75 to 250 °F and pressure of 500 psi.
http://dx.doi.org/10.2118/173745-MS
-
SPE 172018 2014
Fast Hydrating Fracturing Fluid for Ultra High Temperature Reservoirs
Development of a fast-hydrating synthetic copolymer and metal crosslinker capable of maintaining ideal rheological properties for successful fracturing operations at bottom-hole temperatures up to 450°F. M5600 was used to evaluate the actual thermal stability of the fluid at the desired temperature and pressure.
http://dx.doi.org/10.2118/172018-MS
-
SPE 169408 2014
Effect of Dissolved Solids on Reuse of Produced Water in Hydraulic Fracturing Jobs
Introduction of a new viscoelastic acid system which can form gel and maintain its viscosity at temperatures up to 300° F. M5600 was used to obtain a relationship between the rheological properties and crosslink network structure of a fluid.
http://dx.doi.org/10.2118/169408-MS
-
SPE 169141 2014
Enhancing Well Stimulation with Improved Salt Tolerant Surfactant for Bakken Formation
Development of a new stimulation surfactant which will enhance the initial production nd maintain long term production of the middle-member Bakken formation. M5600 was used to test compatibility of surfactant A with several fracturing fluids.
http://dx.doi.org/10.2118/169141-MS
-
SPE 168619 2014
Innovative Use of NMR to Study the Fracture Fluid Propagation in Shale Formation
Determination of the volume of fracturing fluid which is able to propagate inside shale cores based on fracturing fluid viscosity and injection pressures. M5600 was used to measure fluid viscosity.
http://dx.doi.org/10.2118/168619-MS
-
SPE 168614 2014
Effect of Dissolved Solids on Reuse of Produced Water and Proppant Handling in Hydraulic Fracturing Jobs in Tight Sand Gas Reservoirs
Laboratory analysis of dissolved solid contents found in producing water and its effects on borate crosslinked guar-based polymers ability to transport proppant. M5600 was used to measure viscosity of gel at 140 °F and pressure of 300 psi.
http://dx.doi.org/10.2118/168614-MS
-
SPE 168180 2014
Optimizing Surfactant Additives for Enhanced Well Stimulation in Bakken Formation
Laboratory evaluation of stimulation fluid additives and its effectiveness in increasing oil recovery in Bakken formation when used in properly designed fracture treatments. M5600 was used to test compatibility of surfactant A with several fracturing fluids.
http://dx.doi.org/10.2118/168180-MS
-
SPE-168174-MS 2014
Using NMR Technology to Study the Flow of Fracture Fluid inside Shale Formation
Viscosity was measured using a Grace M5600 rheometer.
https://onepetro.org/conference-paper/SPE-168174-MS
-
SPE 167754 2014
New Insights into Shale Fracturing Treatment Design
Study of the effect of various fracture fluid types on Mancos formation hydraulic breakdown pressure. M5600 was used to measure fluid viscosity.
http://dx.doi.org/10.2118/167754-MS
-
IPTC-16689-Abstract 2013
An Effective Acid Placement Technique to Stimulate High-Temperature Sandstone and Carbonate Formations
Measurement viscosity and viscoelastic measurements were performed with a Grace M5600 HPTHT Rheometer.
https://onepetro.org/IPTCONF/proceedings-abstract/12IPTC/All-12IPTC/IPTC-16689-Abstract/154385
-
SPE 165161 2013
Hydrolysis Effect on the Properties of a New Class of Viscoelastic Surfactant-Based Acid and Damage Caused by the Hydrolysis Products
Observations of viscosity changes of viscoelastic surfactant acid systems at high temperatures and the impact of the damage caused by hydrolysis products. M5600 was used to measure the viscosities of the VES-based acids.
http://dx.doi.org/10.2118/165161-MS
-
SPE 165146 2013
Surfactant-Based Fluid-Loss Pills for ZnBr2 Based High-Density Completion Fluids and High-Temperature Applications
Experimental investigation into the ability of a new surfactant system to effectively control fluid loss in high-density brine that contains ZnBr2 solutions at high temperatures up to 300°F. M5600 was used to measure viscosity and viscoelastic properties of surfactant to control fluid loss.
http://dx.doi.org/10.2118/165146-MS
-
Journal of Applied Polymer Science, Volume 127, Issue 5 2013
Preparation and Characterization of Polyacrylamide Nanomicrospheres and Its Profile Control and Flooding Performance
M5600 HPHT rheometer (Grace) was used to measure the storage modulus (G’) and loss modulus (G’’) of the polyacrylamide nanomicrospheres (without solvent) versus temperature and frequency.
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/app.37727
-
Texas A&M University PhD Dissertation 2013
Stimulation of Carbonate Reservoirs Using a New Emulsified Acid System
An HPHT rheometer (Grace M5600) was used to measure the viscosity of live emulsified acids under different conditions. The apparent viscosity of the emulsified acid was measured at 75°F and 220°F for shear rates up to 1000 s-1.
http://oaktrust.library.tamu.edu/bitstream/handle/1969.1/150980/SAYED-DISSERTATION-2013.pdf?sequence=1
-
SPE 157316 2012
Acid Placement: An Effective VES System to Stimulate High-Temperature Carbonate Formations
Through the use of oscillatory rheometer, rotational viscometer, and coreflood tests, rheological properties of a new viscoelastic system which can form gel and maintain its viscosity at temperatures up to 300°F are analyzed. M5600 was used to rheological properties at 300 psi and a temperature range of 75 to 300 °F.
http://dx.doi.org/10.2118/157316-MS
-
SPE 151641 2012
Compatibility and Phase Behavior Studies Between Corrosion Inhibitors and Surfactants-Based Acids
Rheological performance, specifically viscosity, G', and G'', of amine oxide surfactants containing corrosion inhibitors from 75 to 300°F at 300 psi. M5600 was used to measure the rheological properties of live and spent acids under different conditions.
http://dx.doi.org/10.2118/151641-MS
-
Energy Sources, Part A: Recovery, Utilization, and Environmental Effects 2012
An Experiment and Simulation of Elastic Microspheres Enhanced Oil Recovery (EMEOR)
Using an M5600 high pressure and high temperature (HPHT) rheometer (Grace Instrument Company, Houston, TX) the variation of elastic modulus (G0) and viscous modulus (G00) of elastic microspheres versus frequency and temperature was measured.
http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/15567036.2011.592921
-
SPE 148124 2011
Characterization of Self-destructing Filter cake by Using computer Tomography
Measuring the efficiency of filter cake removal method using a water-based drilling fluid system under high pressure high temperature conditions. M5600 was used to measure viscosity of filtrate fluid at 225°F and 300 psi.
http://dx.doi.org/10.2118/148124-MS
-
SPE 143947 2011
A New Technique to Control Fines Migration in Poorly Consolidated Sandstones
Development of a new aqueous chemical system added directly to the treatment fluid in attempt to control migration of fines near wellbore as well as the fracture area. M5600 was used to measure viscosity of borate-crosslink guar and VES fluids.
http://dx.doi.org/10.2118/143947-MS
-
SPE 142264 2011
Impact of Hydrolysis at High Temperatures on the Apparent Viscosity of Carboxybetaine Viscoelastic Surfactant-Based Acid
Study the viscosity alterations of amido-carboxybetaine acid fluids as a result of hydrolysis at high temperatures. M5600 was used to measure apparent viscosity vs. shear rate at 25°C and 1 atm.
http://dx.doi.org/10.2118/142264-MS
-
SPE 135166 (M5500 Rheometer) 2010
Protecting Reservoir with Surfactant Micellar Drill-in Fluids in Carbonate-Contained Formations
Development of a new surfactant micellar-based drilling fluid with internal breakers system in order to drill in carbonate contained reservoirs. M5500 was used to measure viscosity data for the surfactant acid based on DIFs reacting with carbonate and crude oil contact with acid spent surfactant DIF.
http://dx.doi.org/10.2118/135166-MS
-
SPE 128091 2010
Impact of Organic Acids/Chelating Agents on the Rheological Properties of an Amidoamine Oxide Surfactant
Experimental investigation of organic acids and chelating agents used in amidoamine oxide surfactants, and their abilities to affect rheological properties of live and spent acid systems. M5600 was used to measure the apparent viscosity of live and spent acids under different conditions.
http://dx.doi.org/10.2118/128091-MS
-
Chinese Science Bulletin December 2010 Vol.55 No.35: 4074–4082 2010
The mechanism for fuzzy-ball working fluids for controlling & killing lost circulation
Rheological experiment of fuzzy ball working fluid. ZNN-D6 rotation viscometer (Qingdao Tongchun Petroleum Instrument Co., LTD), M5600 HPHT rheometer (USA, Grace, Instrument).
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11434-010-3202-8
-
SPE 124704 2009
Design Criteria and Application of High Density, Brine Based Fracturing Fluid for Deepwater Frac and Packs
Analysis of fluid rheology, proppant transport, and fluid compatibility of high-density brine-based fluids implemented in deepwater Gulf of Mexico wells.
http://dx.doi.org/10.2118/124704-MS
-
SPE 121716 2009
Rheological Properties of a New Class of Viscoelastic Surfactant
Examination of the rheological properties of a new type of viscoelastic amphoteric surfactant, amine oxide, at temperatures from 75-220°F at 300 psi and various shear rates from 0.01-935 1/sec. M5600 measured the apparent viscosity of live and spend acids under different conditions.
http://dx.doi.org/10.2118/121716-MS
-
SPE 112484 (M5500 Rheometer) 2008
Do Viscoelastic-Surfactant Diverting Fluids for Acid Treatments Need Internal Breakers?
Introduction of a viscoelastic organic acid fluid, with internal breakers, capable of treating carbonate reservoirs and assuring complete treatment fluid cleanup. M5500 was used to generate rheological data with pressure and temperature.
http://dx.doi.org/10.2118/112484-MS
-
SPE 107728 2007
Nanotechnology Applications in Viscoelastic Surfactant Stimulation Fluids
Nanotechnology application in viscoelastic stimulation fluid system in order to maintain rheological properties at high temperatures as well as controlling fluid loss without formation damage.
http://dx.doi.org/10.2118/107728-MS
-
SPE 105815 2007
Anionic Surfactant Gel Treatment Fluid
Rheological testing of anionic viscoelastic surfactant and performance of the system due to the effects of temperature, salt concentrations and co-surfactants.
http://dx.doi.org/10.2118/105815-MS
-
SPE 93536 (M5500 Rheometer) 2005
A Case Study of a Successful Matrix Acid Stimulation Treatment in Horizontal Wells Using a New Diversion Surfactant in Saudi Arabia
Examination of the rheological properties of brines, foams, and spent acids composed of a new class of viscoelastic surfactants, as well as the diversion abilities of each system.
http://dx.doi.org/10.2118/93536-MS
-
SPE 93449 (M5500 Rheometer) 2005
Internal Phase Breaker Technology for Viscoelastic Surfactant Gelled Fluids
Implementation of viscosity break tests to gather rheological data of a breaker system for complete and controllable reduction of viscoelastic gel viscosity at temperatures from 80° to 225° F.
http://dx.doi.org/10.2118/93449-MS
